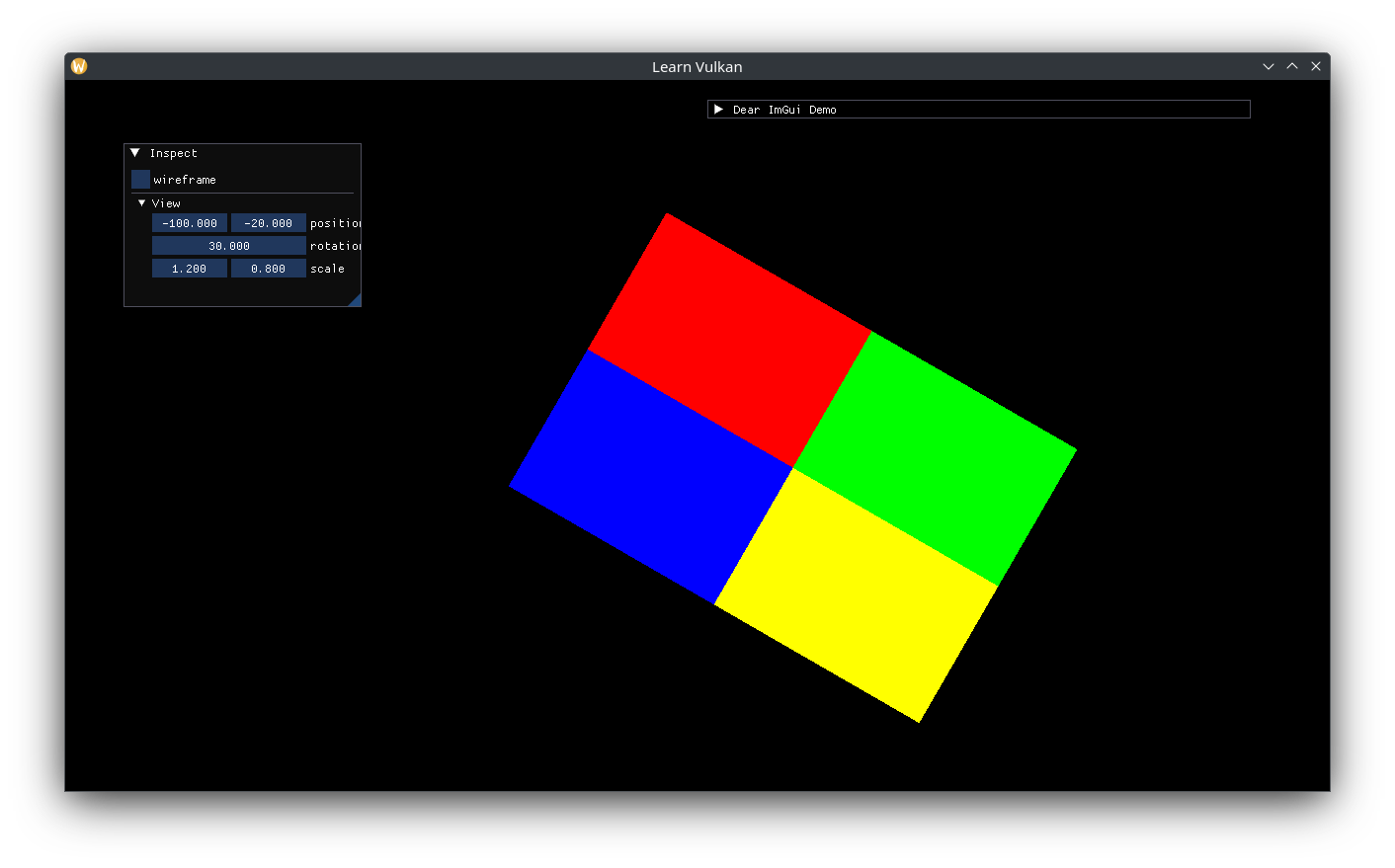
View Matrix
Integrating the view matrix will be quite simple and short. First, transformations for objects and cameras/views can be encapsulated into a single struct:
struct Transform {
glm::vec2 position{};
float rotation{};
glm::vec2 scale{1.0f};
[[nodiscard]] auto model_matrix() const -> glm::mat4;
[[nodiscard]] auto view_matrix() const -> glm::mat4;
};
Extracting the common logic into a helper, both member functions can be implemented easily:
namespace {
struct Matrices {
glm::mat4 translation;
glm::mat4 orientation;
glm::mat4 scale;
};
[[nodiscard]] auto to_matrices(glm::vec2 const position, float rotation,
glm::vec2 const scale) -> Matrices {
static constexpr auto mat_v = glm::identity<glm::mat4>();
static constexpr auto axis_v = glm::vec3{0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f};
return Matrices{
.translation = glm::translate(mat_v, glm::vec3{position, 0.0f}),
.orientation = glm::rotate(mat_v, glm::radians(rotation), axis_v),
.scale = glm::scale(mat_v, glm::vec3{scale, 1.0f}),
};
}
} // namespace
auto Transform::model_matrix() const -> glm::mat4 {
auto const [t, r, s] = to_matrices(position, rotation, scale);
// right to left: scale first, then rotate, then translate.
return t * r * s;
}
auto Transform::view_matrix() const -> glm::mat4 {
// view matrix is the inverse of the model matrix.
// instead, perform translation and rotation in reverse order and with
// negative values. or, use glm::lookAt().
// scale is kept unchanged as the first transformation for
// "intuitive" scaling on cameras.
auto const [t, r, s] = to_matrices(-position, -rotation, scale);
return r * t * s;
}
Add a Transform member to App to represent the view/camera, inspect its members, and combine with the existing projection matrix:
Transform m_view_transform{}; // generates view matrix.
// ...
ImGui::Separator();
if (ImGui::TreeNode("View")) {
ImGui::DragFloat2("position", &m_view_transform.position.x);
ImGui::DragFloat("rotation", &m_view_transform.rotation);
ImGui::DragFloat2("scale", &m_view_transform.scale.x);
ImGui::TreePop();
}
// ...
auto const mat_view = m_view_transform.view_matrix();
auto const mat_vp = mat_projection * mat_view;
auto const bytes =
std::bit_cast<std::array<std::byte, sizeof(mat_vp)>>(mat_vp);
m_view_ubo->write_at(m_frame_index, bytes);
Naturally, moving the view left moves everything else - currently only a single RGBY quad - to the right.